Dart 学习笔记
作为学习 Flutter 的语法。
语法
Dart 与 Javascript 不同,结尾必须有 " ; "
Dart变量
在 dart 中,使用以下关键词定义变量
var:自动类型检测,不支持改变数据类型的重新赋值
String:字符串类型,可以是单引号和双引号
int:数字类型
定义常量:
const:定义时就需要赋值,并且:Const 变量必须使用常量值进行初始化。
const关键词在多个地方创建相同的对象的时候,内存中只保留了一个对象
final:开始时可以不赋值,只能赋值一次,不仅有const的特性,同时只有在使用前才会进行初始化
‼️注意:
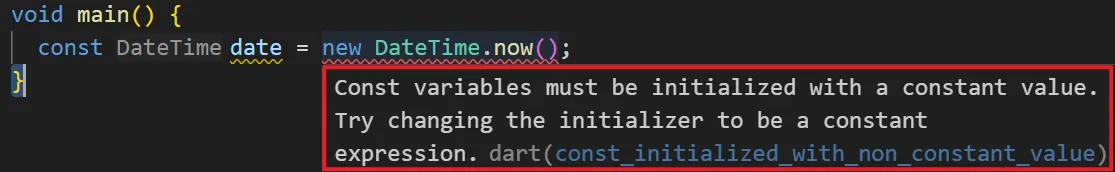
使用const会出现报错
const定义的变量必须严格
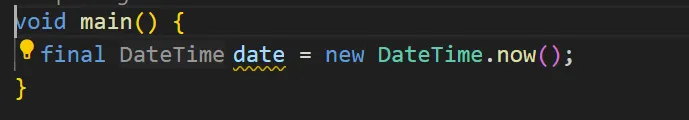
入口
Dart中使用 main 作为入口方法
有两种写法:
main() {
print('hello dart')
}OR:
void main() {
print('hello dart')
}类型
常用类型
Numbers:数值类型
int
double
String:字符串
String
String str1='你好';
String str2='Dart';
String str3="""
this is str1
this is str1
this is str1
""";
print("$str1 $str2");
print(str1 + str2);
print(str1 +" "+ str2);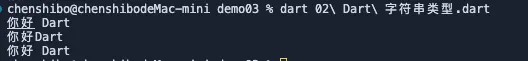
Booleans:布尔类型
bool
不会进行自动类型转换对比:
var a = '123';
var b = 123;
if (a == b) {
print('a=b');
} else {
print('a!=b');
}
List:数组,也是列表
可以不指定类型数组:
var arr = ['张三', 20, true]可以指定类型:
var arr = <int>[1, 2]var arr1 = <String>['张三‘, '李四']数组长度可以增加:
arr.add(1)使用 List.filled 创建的数组长度固定:
var arr = List.filled(2, "")且不能修改长度
Maps:字典/对象类型
使用 Object 创建对象
var person = {
"name": "张三",
"age": 20,
"work": ["程序员", "外卖员"]
};使用 Maps 定义
var p = new Map()
p["name"] = "李四";
p["age"] = 20;
p["work"] = ["程序员", "外卖员"];
print(p);
print(p["age"];不能使用 p.age 的方式进行取用
不常用类型
Runes
Rune是UTF-32编码的字符串。它可以通过文字转换成符号表情或者代表特定的文字。
void main() {
var clapping = '\u{1f44f}';
print(clapping);
print(clapping.codeUnits);
print(clapping.runes.toList());
Runes input = new Runes(
'\u2665 \u{1f605} \u{1f60e} \u{1f47b} \u{1f596} \u{1f44d}');
print(new String.fromCharCodes(input));
}输出为: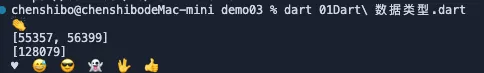
Symbols
Symbol对象表示在Dart程序中声明的运算符或标识符。您可能永远不需要使用符号,但它们对于按名称引用标识符的API非常有用,因为缩小会更改标识符名称而不会更改标识符符号。要获取标识符的符号,请使用符号文字,它只是#后跟标识符:
类型推断
使用 is 关键词进行推断
var str = 123;
if (str is String) {
print('是string类型');
} else if (str is int) {
print('int');
} else {
print('其他类型');
}类型转换
String and Numbers
String str = '123';
var myNum=int.parse(str);
print(myNum is int);
String str = '123.1';
var myNum=double.parse(str);
print(myNum is double);var myNum = 12;
var str = myNum.toString();
print(str is String);To Booleans
var str = '';
if(str.isEmpty){
print('str空');
}else{
print('str不为空');
}运算符
赋值运算符
其他运算符与其他语言一样,仅写不一样的
??=使用 int? 声明可为 null 的整数类型,并初始化为 null
int? b;
b ??= 23;
print(b);条件运算符
其他运算符与其他语言一样,仅写不一样的
??如果左侧值为 null,取右侧值。
int? b;
b ??= 23;
print(b);高级类型
List
常用属性
length 长度
reversed 翻转
isEmpty 是否为空
isNotEmpty 是否不为空
常用方法
add 增加
addAll 拼接数组
indexOf 查找 传入具体值
remove 删除 传入具体值
removeAt 删除 传入索引值
fillRange 修改
insert(index, value)指定位置插入insertAll(index, list)指定位置插入全部toList 其他类型转换成 List 类型
join List 转换成字符串
split() 字符串转换成 List
forEach 遍历 List
map 遍历 List,返回新 List
where 筛选,相当于 JS 中的 filter
any 检查列表中是否有至少一个元素满足给定的条件,相当于 JS 中的 some
every 检查列表中的所有元素是否都满足给定的条件
Set
最主要的作用就是对数组进行去重
List myList=['香蕉','苹果','西瓜','香蕉','苹果','香蕉','苹果'];
var s=new Set();
s.addAll(myList);
print(s);
print(s.toList());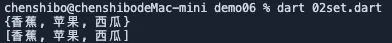
Map
常用属性
keys 获取所有的 key 值
values 获取所有的 value值
isEmpty 是否为空
isNotEmpty 是否不为空
常用方法
remove(key)删除指定 key 的数据addAll({})合并映射 给映射内增加属性containsValue 看映射中是否包含某值,返回 true/false
forEach
map
any
where
every
方法
方法的定义
void printInfo(){
print('我是一个自定义方法');
}
int getNum(){
var myNum=123;
return myNum;
}
String printUserInfo(){
return 'this is str';
}
List getList(){
return ['111','2222','333'];
}方法传参
可选参数
String printUserInfo(String username,[int? age]){ //行参
return "姓名:$username---年龄:$age";
}
print(printUserInfo('张三',21)); //实参
print(printUserInfo('张三'));
默认参数
String printUserInfo(String username,[int age = 0]){ //行参
return "姓名:$username---年龄:$age";
}
print(printUserInfo('张三',21)); //实参
print(printUserInfo('张三'));
箭头函数
注意和方法的区别: 箭头函数内只能写一条语句,并且语句后面没有分号(;)
List list=['苹果','香蕉','西瓜'];
list.forEach((value){
print(value);
});
list.forEach((value)=>print(value));list.forEach((value)=>{
print(value)
});面向对象
Dart 所有的东西都是对象,所有的对象都继承自 Object 类。
Dart 是一门使用类和单继承的面向对象语言,所有的对象都是类的实例,并且所有的类都是 Object 的字类。
Class 类
基础用法
class Person {
String name = '张三';
int age = 23;
void getInfo() {
print("${this.name}, ${this.age}");
}
void setInfo(int age) {
this.age = age
}
}
void main() {
Person p1 = new Person();
p1.setInfo(25);
p1.getInfo();
}构造函数
构造函数中的内容,会在类被实例化时调用。
默认使用
class Person {
String name = '张三';
int age = 20;
Person() {
print("这是构造函数中的内容");
}
void printInfo() {
print("${this.name}, ${this.age}");
}
}初始化类
dart 中需要初始化不可为 null 的实例字段,如果不初始化的话需要在属性前面加上late
class Person {
late String name;
late int age;
Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
// 或者直接这样写:
// Person(this.name, this.age)
void printInfo() {
print("${this.name}, ${this.age}");
}
}
void main() {
Person p1 = new Person('张三', 20);
p1.printInfo();
}自定义命名构造函数
dart里面构造函数可以写多个
class Person {
late String name;
late int age;
//默认构造函数的简写
Person(this.name, this.age);
Person.now() {
print('我是命名构造函数');
}
Person.setInfo(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
void printInfo() {
print("${this.name}----${this.age}");
}
}
void main() {
// var d=new DateTime.now(); //实例化DateTime调用它的命名构造函数
// print(d);
//Person p1=new Person('张三', 20); //默认实例化类的时候调用的是 默认构造函数
//Person p1=new Person.now(); //命名构造函数
Person p1 = new Person.setInfo('李四', 30);
p1.printInfo();
}
抽离类为单独模块
// 注意:最新版本的dart中需要初始化不可为null的实例字段,如果不初始化的话需要在属性前面加上late
class Person{
late String name;
late int age;
//默认构造函数的简写
Person(this.name,this.age);
Person.now(){
print('我是命名构造函数');
}
Person.setInfo(String name,int age){
this.name=name;
this.age=age;
}
void printInfo(){
print("${this.name}----${this.age}");
}
}引入:
import 'lib/Person.dart';
void main(){
Person p1 = new Person.setInfo('李四1', 30);
p1.printInfo();
}私有方法、公用方法
dart 中没有像是 java 中 public, private 这种关键词。
在这里使用 _ 前缀命名将属性或方法定义为私有。
class Animal{
late String _name; //私有属性
late int age;
//默认构造函数的简写
Animal(this._name,this.age);
void printInfo(){
print("${this._name}----${this.age}");
}
String getName(){
return this._name;
}
void _run(){
print('这是一个私有方法');
}
execRun(){
this._run(); //类里面方法的相互调用
}
}
void main(){
Animal a = new Animal('小狗', 3);
print(a.getName());
a.execRun(); //间接的调用私有方法
}getter, setter
dart 中,使用 get,set 关键词作为 getter 和 setter。
class Rectangle {
double _width;
double _height;
Rectangle(this._width, this._height);
// Getter for width
double get width => _width;
// Setter for width
set width(double value) {
if (value > 0) {
_width = value;
} else {
throw ArgumentError("Width must be greater than zero");
}
}
// Getter for height
double get height => _height;
// Setter for height
set height(double value) {
if (value > 0) {
_height = value;
} else {
throw ArgumentError("Height must be greater than zero");
}
}
// A computed property
double get area => _width * _height;
}void main() {
var rect = Rectangle(5, 10);
// 使用 getter 获取值
print('Width: ${rect.width}'); // 输出: Width: 5.0
print('Height: ${rect.height}'); // 输出: Height: 10.0
print('Area: ${rect.area}'); // 输出: Area: 50.0
// 使用 setter 设置值
rect.width = 7;
rect.height = 14;
print('Updated Width: ${rect.width}'); // 输出: Updated Width: 7.0
print('Updated Height: ${rect.height}'); // 输出: Updated Height: 14.0
print('Updated Area: ${rect.area}'); // 输出: Updated Area: 98.0
// 尝试设置无效的值,将抛出异常
try {
rect.width = -3; // 这将抛出异常
} catch (e) {
print(e); // 输出: Invalid argument(s): Width must be greater than zero
}
}类的默认初始化
// Dart中我们也可以在构造函数体运行之前初始化实例变量
class Rect {
int height;
int width;
Rect():height = 2, width = 10{
print("${this.height}---${this.width}");
}
getArea(){
return this.height * this.width;
}
}
void main(){
Rect r = new Rect();
print(r.getArea());
}也可以这样:
class Rect {
int height;
int width;
Rect([this.height = 2, this.width = 10]);
get area => this.height * this.width;
}
void main() {
Rect r = new Rect(10, 20);
print(r.area);
}亦可以这样:
class Rect {
int height;
int width;
Rect({this.height = 2, this.width = 10}){}
get area => this.height * this.width;
}
void main() {
Rect r = new Rect(height: 3, width: 5);
print(r.area);
}
可选参数传递方式:
🌟位置参数(Positional Parameters):
这是最常见的一种参数传递方式。参数按顺序传递给函数或构造函数。
分为两种:
必需位置参数:没有默认值,调用时必须提供。
可选位置参数:用方括号 [] 包围,并可以提供默认值,不传递时使用默认值
🌟命名参数(Named Parameters)
参数以名称进行标识,调用时通过名字指定。
用大括号 {} 包围,可以显式地标明每个参数的含义。
命名参数通常是可选的,但它们也可以设置为必需的(使用 required 关键字)。
🌟总结
位置参数适合于参数意义明确且顺序固定的情况。
命名参数则更灵活,尤其适用于多个可选参数或者需要提高代码可读性的时候。
常量构造函数
常量构造函数需以const关键字修饰
const构造函数必须用于成员变量都是final的类
如果实例化时不加const修饰符,即使调用的是常量构造函数,实例化的对象也不是常量实例
实例化常量构造函数的时候,多个地方创建这个对象,如果传入的值相同,只会保留一个对象。
Flutter中const 修饰不仅仅是节省组件构建时的内存开销,Flutter 在需要重新构建组件的时候,由于这个组件是不应该改变的,重新构建没有任何意义,因此 Flutter 不会重建构建 const 组件
//常量构造函数
class Container{
final int width;
final int height;
const Container({required this.width,required this.height});
}
void main(){
var c1=Container(width: 100,height: 100);
var c2=Container(width: 100,height: 100);
print(identical(c1, c2)); //false
var c3=const Container(width: 100,height: 100);
var c4=const Container(width: 100,height: 100);
print(identical(c3, c4)); //true
var c5=const Container(width: 100,height: 110);
var c6=const Container(width: 120,height: 100);
print(identical(c5, c6)); //false
}静态成员
dart 中使用 static 关键词实现静态方法及变量。
静态方法不能访问非静态成员,非静态方法可以访问静态成员
使用 static 定义的属性或方法可以直接使用 类.方法 来使用
class Person {
static String name = '张三';
static void show() {
print(name);
}
static void printUserInfo(){//静态方法
print(name); //静态属性
show(); //静态方法
}
}
void main() {
print(Person.name);
Person.show();
}对象操作符
Dart 中的对象操作符:
as 类型转换
is 类型判断
.. 级联操作(连缀)
class Person {
String name;
num age;
Person(this.name, this.age);
void printInfo() {
print("${this.name}---${this.age}");
}
}
void main() {
Person p1 = new Person('张三1', 20);
p1.printInfo();
p1
..name = "李四"
..age = 30
..printInfo();
}继承
简单继承
使用 extends 关键词来继承父类。
不会继承父类的构造函数。
class Person {
String name='张三';
num age=20;
void printInfo() {
print("${this.name}---${this.age}");
}
}
class Web extends Person{
}
main(){
Web w=new Web();
print(w.name);
w.printInfo();
}super传参
使用 super 关键字继承父类的构造函数
class Person {
late String name;
late num age;
Person(this.name, this.age);
void printInfo() {
print("${this.name}---${this.age}");
}
}
class Web extends Person {
Web(String name, num age) : super(name, age) {}
}
main(){
Web w=new Web('张三', 12);
w.printInfo();
}class Person {
String name;
num age;
Person(this.name, this.age);
void printInfo() {
print("${this.name}---${this.age}");
}
}
class Web extends Person{
late String sex;
Web(String name, num age, String sex) : super(name, age){
this.sex=sex;
}
run(){
print("${this.name}---${this.age}--${this.sex}");
}
}
main(){
Web w=new Web('张三', 12, "男");
w.printInfo();
w.run();
}命名构造函数传参
class Person {
String name;
num age;
Person(this.name, this.age);
Person.xxx(this.name, this.age);
void printInfo() {
print("${this.name}---${this.age}");
}
}
class Web extends Person {
late String sex;
Web(String name, num age, String sex) : super.xxx(name, age) {
this.sex = sex;
}
run() {
print("${this.name}---${this.age}--${this.sex}");
}
}重写父类方法
重写父类方法使用@override注解(可以不写,最好写上)
class Person {
String name;
num age;
Person(this.name,this.age);
void printInfo() {
print("${this.name}---${this.age}");
}
work(){
print("${this.name}在工作...");
}
}
class Web extends Person{
Web(String name, num age) : super(name, age);
run(){
print('run');
}
//覆写父类的方法
@override //可以写也可以不写 建议在覆写父类方法的时候加上 @override
void printInfo(){
print("姓名:${this.name}---年龄:${this.age}");
}
@override
work(){
print("${this.name}的工作是写代码");
}
}字类调用父类方法
使用super.xxx()调用父类的方法
class Person {
String name;
num age;
Person(this.name,this.age);
void printInfo() {
print("${this.name}---${this.age}");
}
work(){
print("${this.name}在工作...");
}
}
class Web extends Person{
Web(String name, num age) : super(name, age);
run(){
print('run');
super.work(); //子类调用父类的方法
}
//覆写父类的方法
@override //可以写也可以不写 建议在覆写父类方法的时候加上 @override
void printInfo(){
print("姓名:${this.name}---年龄:${this.age}");
}
}抽象类
Dart 中抽象类主要用于定义标准,子类可以继承抽象类,也可以实现抽象类接口。
抽象类通过
abstract关键字定义Dart 中的抽象方法不能用
abstract声明,Dart 中没有方法体的方法成为抽象方法如果子类继承抽象类必须得实现里边的抽象方法
如果把抽象类当做接口实现的话必须得实现抽象类里面定义的所有属性和方法
抽象类不能被实例化,只有继承他的子类可以
extends抽象类 和 implements的区别:
extends
继承父类:使用 extends 关键字时,子类继承了父类的实现和接口(即方法和属性)。子类可以重写父类的方法,也可以调用父类的方法。
单继承:Dart 类不能继承多个类,因此一个类只能 extends 一个直接父类。
访问控制:子类可以访问父类的受保护成员(前缀为 _ 的变量和方法)。
抽象类:如果父类是抽象类,它可以包含没有实现的方法,这些方法必须在非抽象子类中实现。
abstract class Animal {
void breathe() {
print("Breathing");
}
void makeSound(); // 抽象方法
}
class Dog extends Animal {
@override
void makeSound() {
print("Bark");
}
}implements
实现接口:使用 implements 时,类必须实现接口中的所有方法和属性。任何类(包括普通类)都可以被用作接口。
多接口实现:一个类可以实现多个接口,即可以 implements 多个类。
不继承实现:使用 implements 时,子类不会继承接口类的实现,只需提供接口中定义的所有方法和属性的具体实现。
class Animal {
void breathe() {
print("Breathing");
}
void makeSound() {
print("Animal sound");
}
}
class Bird {
void fly() {
print("Flying");
}
}
class Robot implements Animal, Bird {
@override
void breathe() {
print("Robot breathing");
}
@override
void makeSound() {
print("Beep Boop");
}
@override
void fly() {
print("Rocket flying");
}
}多态
允许将子类类型的指针赋值给父类类型的指针, 同一个函数调用会有不同的执行效果 。
子类的实例赋值给父类的引用。
多态就是父类定义一个方法不去实现,让继承他的子类去实现,每个子类有不同的表现。
abstract class Animal{
eat(); //抽象方法
}
class Dog extends Animal{
@override
eat() {
print('小狗在吃骨头');
}
run(){
print('run');
}
}
class Cat extends Animal{
@override
eat() {
print('小猫在吃老鼠');
}
run(){
print('run');
}
}
main() {
Animal d=new Dog();
d.eat();
Animal c=new Cat();
c.eat();
}接口
在 Dart 中,没有 interface 等关键词定义接口,我们使用抽象类定义接口。
abstract class Db{ //当做接口 接口:就是约定 、规范
late String uri; //数据库的链接地址
add(String data);
save();
delete();
}
class Mysql implements Db{
@override
String uri;
Mysql(this.uri);
@override
add(data) {
// TODO: implement add
print('这是mysql的add方法'+data);
}
@override
delete() {
// TODO: implement delete
return null;
}
@override
save() {
// TODO: implement save
return null;
}
remove(){
}
}
class MsSql implements Db{
@override
late String uri;
@override
add(String data) {
print('这是mssql的add方法'+data);
}
@override
delete() {
// TODO: implement delete
return null;
}
@override
save() {
// TODO: implement save
return null;
}
}
main() {
Mysql mysql=new Mysql('xxxxxx');
mysql.add('1243214');
}使用 mixins 实现多继承
在 Dart 中可以使用 mixins 实现多继承
作为 mixins 的类只能继承自 Object,不能继承其他类
作为 mixins 的类不能有构造函数
一个类可以 mixins 多个 mixins 类
mixins 类需要以
mixin关键字定义
mixin class A {
String info="this is A";
void printA(){
print("A");
}
}
mixin class B {
void printB(){
print("B");
}
}
class C with A,B{}
void main(){
var a = new A();
a.printA();
var c=new C();
c.printA();
c.printB();
print(c.info);
}
可以继承再混入
class Person{
String name;
num age;
Person(this.name,this.age);
printInfo(){
print('${this.name}----${this.age}');
}
void run(){
print("Person Run");
}
}
mixin class A {
String info="this is A";
void printA(){
print("A");
}
void run(){
print("A Run");
}
}
mixin class B {
void printB(){
print("B");
}
void run(){
print("B Run");
}
}
class C extends Person with B,A{
C(String name, num age) : super(name, age);
}
void main(){
var c=new C('张三',20);
c.printInfo();
c.run();
}混入类型判断为 true
mixin class A {
String info="this is A";
void printA(){
print("A");
}
}
mixin class B {
void printB(){
print("B");
}
}
class C with A,B{}
void main(){
var c=new C();
print(c is C); //true
print(c is A); //true
print(c is B); //true
}泛型
泛型就是为了提高 类、接口、方法的复用性。
泛型方法
getData<T>(T value){
return value;
}
void main(){
print(getData<int>(12));
}泛型类
class MyList<T> {
List list = <T>[];
void add(T value) {
this.list.add(value);
}
List getList() {
return list;
}
}
main() {
MyList l2 = new MyList<String>();
l2.add("张三");
print(l2.getList());
}泛型接口
abstract class Cache<T> {
getByKey(String key);
void setByKey(String key, T value);
}
class MemoryCache<T> implements Cache<T> {
@override
getByKey(String key) {
return null;
}
@override
void setByKey(String key, T value) {
print("我是内存缓存 把key=${key} value=${value} -写入到了内存中");
}
}
void main() {
MemoryCache m = new MemoryCache<Map>();
m.setByKey('index', {"name": "张三", "age": 20});
}使用库
在 Dart 中导入库使用 import 关键字
导入本地库
class Animal{
String _name; //私有属性
int age;
//默认构造函数的简写
Animal(this._name,this.age);
void printInfo(){
print("${this._name}----${this.age}");
}
String getName(){
return this._name;
}
void _run(){
print('这是一个私有方法');
}
execRun(){
this._run(); //类里面方法的相互调用
}
}import 'lib/Animal.dart';
main(){
var a=new Animal('小黑狗', 20);
print(a.getName());
}导入系统库
import "dart:math";
main(){
print(min(12,23));
print(max(12,25));
}系统内置实现 HTTP 请求
// 解码响应内容
import 'dart:convert';
// HTTP 请求
import 'dart:io';
void main() async{
var result = await getDataFromZhihuAPI();
print(result);
}
//api接口: http://news-at.zhihu.com/api/3/stories/latest
getDataFromZhihuAPI() async{
//1、创建HttpClient对象
var httpClient = new HttpClient();
//2、创建Uri对象
var uri = new Uri.http('news-at.zhihu.com','/api/3/stories/latest');
//3、发起请求,等待请求
var request = await httpClient.getUrl(uri);
//4、关闭请求,等待响应
var response = await request.close();
//5、解码响应的内容
return await response.transform(utf8.decoder).join();
}async/await
使用方法和 JavaScript 相同
导入三方库(Pub)
使用:
需要在自己想项目根目录新建一个pubspec.yaml
pubspec.yaml文件 然后配置名称 、描述、依赖等信息
然后运行 pub get 获取包下载到本地
项目中引入库 import 'package:http/http.dart' as http; 看文档使用
安装:
dart:
dart pub add http; flutter:flutter pub add http
这个操作将会在 pubspec.yaml 文件上添加这么一行:
dependencies:
http: ^1.2.2引入使用:
import 'package:http/http.dart';
部分导入
只导入需要的部分,使用show关键字,如下例子所示
import 'package:lib1/lib1.dart' show foo;
隐藏不需要的部分,使用hide关键字,如下例子所示:
import 'package:lib2/lib2.dart' hide foo;
延迟加载/懒加载
可以在需要的时候再进行加载。
懒加载的最大好处是可以减少APP的启动时间。
懒加载使用deferred as关键字来指定,如下例子所示:
import 'package:deferred/hello.dart' deferred as hello;
当需要使用的时候,需要使用loadLibrary()方法来加载:
greet() async {
await hello.loadLibrary();
hello.printGreeting();
}Null Safety
Dart 的空安全(Null Safety)是一项语言特性,旨在帮助开发者避免运行时空引用错误。这是通过在编译时捕获潜在的空值问题来实现的。以下是空安全的一些关键概念和特性:
我感觉就很想 JS 中对于 Null 值的控制。
非空类型
默认情况下,Dart 中的所有变量都被认为是非空的,即它们不能为 null。例如:
int number = 42; // number 不能为 null。如果尝试将 null 赋值给一个非空类型的变量,编译器会报错。
可空类型
如果需要让变量可以为 null,则必须显式地将类型标记为可空。在 Dart 中,你可以通过在类型后面加上问号 ? 来表示该类型可以为 null:
int? nullableNumber = null; // nullableNumber 可以为 null。空安全运算符
为了方便处理可能为空的变量,Dart 提供了一些特殊的运算符:
条件访问 (?.): 用于在调用对象的方法或属性之前检查对象是否为 null。
String? name;
print(name?.length); // 如果 name 为 null,则结果为 null,否则返回 length。如果为空 (??): 用于在一个表达式可能为 null 时提供默认值。
String? name;
String displayName = name ?? 'Guest';如果为空赋值 (??=): 用于仅在变量为 null 时进行赋值。
String? name;
name ??= 'Guest'; // 如果 name 为 null,则赋值 'Guest'。非空断言
当你确定某个可空变量在某个点上不可能为 null 时,可以使用 ! 运算符来断言其非空性:
String? name;
print(name!.length); // 假设我们确定 name 不为 null,否则会抛出异常。Required
required关键词:
最开始 @required 是注解
现在它已经作为内置修饰符。
主要用于允许根据需要标记任何命名参数(函数或类),使得它们不为空。因为可选参数中必须有个 required 参数 或者 该参数有个默认值。
String printUserInfo(String username, {int age=10, String sex="男"}) {//行参
return "姓名:$username---性别:$sex--年龄:$age";
}
String printInfo(String username, {required int age, required String sex}) {//行参
return "姓名:$username---性别:$sex--年龄:$age";
}
void main(args) {
print(printUserInfo('张三'));
print(printUserInfo('张三',sex: "女"));
print(printInfo('张三',sex: "女", age: null));
}




